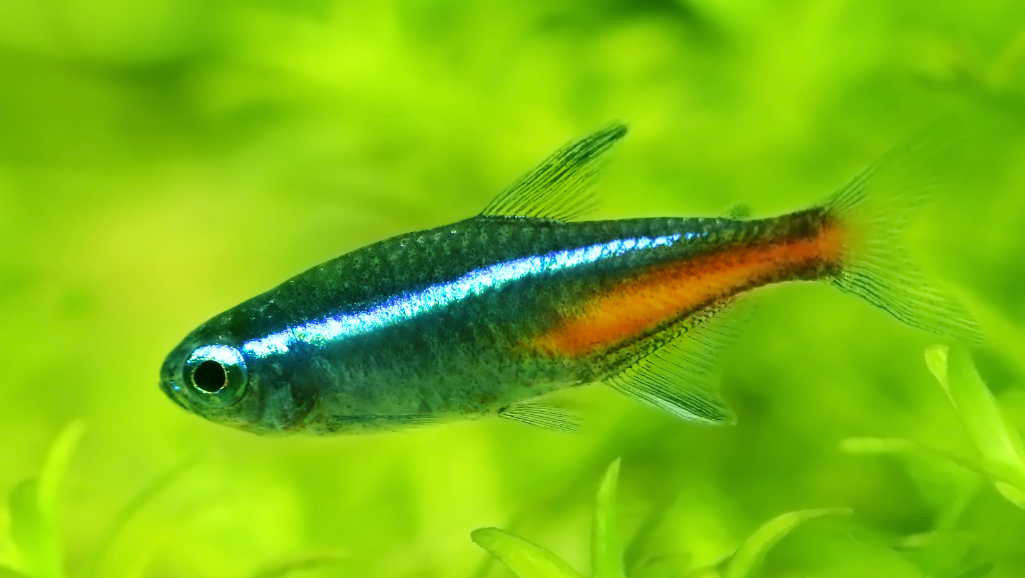
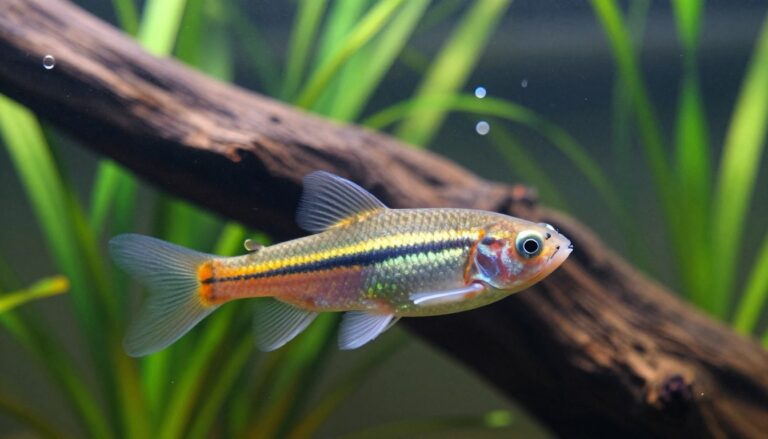
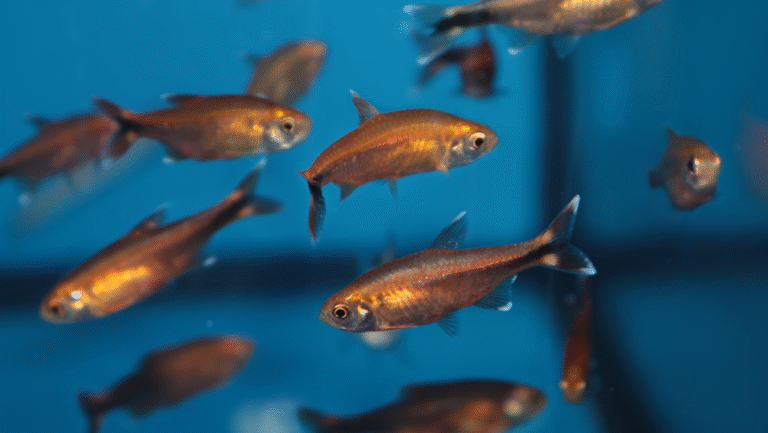
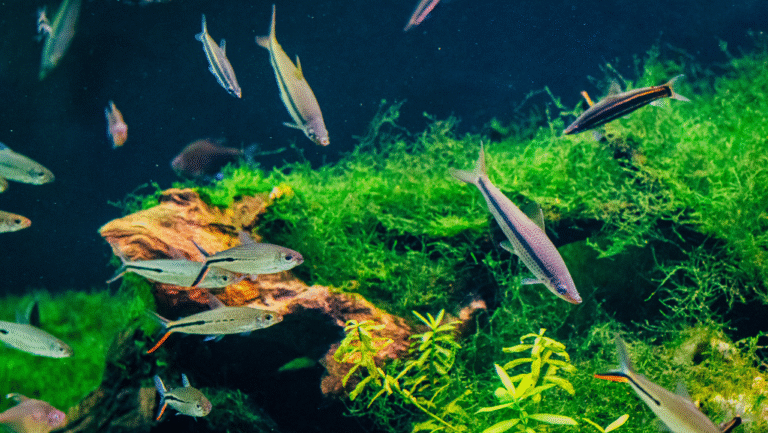
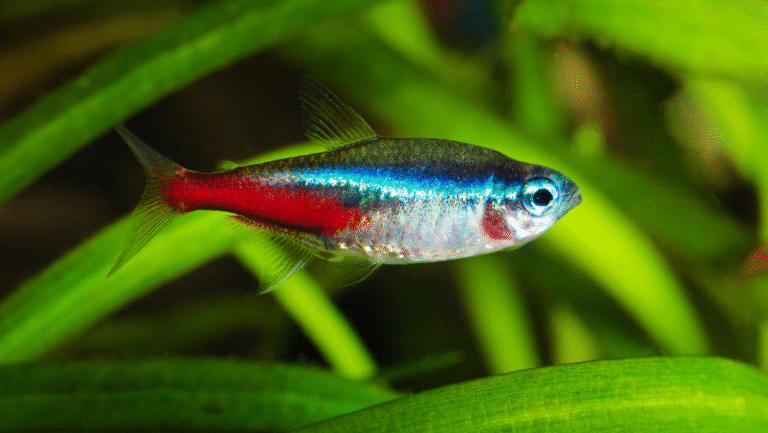
The Neon Tetra is one of the most recognizable freshwater fish, prized for its iridescent blue stripe and vivid red band. Native to the Amazon basin (rivers and tributaries in countries such as Colombia, Brazil, and Peru), these small, peaceful fish bring lively schooling behavior and bright color to planted aquariums.
Caring for neon tetras means more than admiring their colors — it means building an environment that matches their natural habitat. That involves stable water chemistry, suitable tank size, compatible tankmates, and proper feeding so your neon tetras can thrive and display their best color.
Neon tetras prefer soft, slightly acidic water; monitoring water parameters regularly helps prevent stress and disease. Choose calm, non-aggressive fish as companions, feed a varied diet, and provide planted, dimly lit spaces that mimic their blackwater/clearwater origins.
With consistent care, neon tetras commonly live around 4–6 years in captivity; some individuals may reach longer lifespans with optimal conditions. Creating the right environment—temperature, pH, hardness, filtration, and group size—will maximize their health and longevity.
Key Takeaways
- Neon Tetra Care: aim for a stable temperature (about 74–79°F / 23–26°C) and slightly acidic to neutral pH (around 5.5–7.0).
- Tank size: provide at least a 10–20 gallon (≈40–75 L) aquarium for a small school; larger tanks are better for visible schooling behavior.
- Water parameters and routine testing are essential—monitor pH, temperature, and hardness to keep your fish thriving.
- Diet: offer varied foods (quality flakes, occasional live/frozen brine shrimp and bloodworms) to keep colors vibrant.
- Group neon tetras in schools (6+ individuals) so they feel secure and show natural schooling behavior.
- Recreate blackwater-like conditions (plants, driftwood, subdued lighting) when breeding is the goal.
- Protect their wild habitat: conservation of Amazonian ecosystems supports this species in the wild.
Understanding the Neon Tetra: An Introduction
Neon tetras (Paracheirodon innesi) are one of the most popular small freshwater fish because of their striking iridescent blue stripe and bright red band. These tetras are a schooling species that display graceful, synchronized swimming when kept in groups — a major reason hobbyists add neon tetras to planted community tanks.
The Mesmerizing Appearance of Neon Tetras
Neon tetras are instantly recognizable: a slender body with a shimmering electric-blue stripe from snout to adipose fin and a vivid red stripe along the lower half of the body. Adults typically reach about 1.2–1.5 inches (3–3.8 cm) in length. Those visual cues — the blue “neon” line and red tail area — are what make neon tetras so eye-catching under subdued aquarium lighting.
Origins and Natural Habitat of Neon Tetras
The natural Neon Tetra habitat is the blackwater and clearwater tributaries of the Amazon Basin in South America (places in Colombia, Brazil, and Peru). In the wild they live in soft, acidic water shaded by dense vegetation and leaf litter; reproducing those conditions in the tank (soft water, tannin-rich driftwood, lots of plants, low light) helps neon tetras feel secure and show their best color. For further reading, see Keeping Tropical Fish.
Social and Behavioral Aspects of Neon Tetras
Neon tetra behavior is strongly social: they are true schooling fish and should be kept in groups. A minimum school size of six is often recommended for visible schooling and reduced stress, though larger groups (10+) produce more natural behavior and a striking visual effect. With consistent care and stable water conditions, neon tetras commonly live about 4–6 years in captivity; a few well-cared-for individuals may live longer.
Routine maintenance — regular water changes, monitoring of water parameters, and gentle filtration — keeps neon tetras healthy and reduces the chance of disease. Helpful maintenance tips and cleaning tools can be found at Aqua Joy Life.
Creating the Perfect Neon Tetra Environment
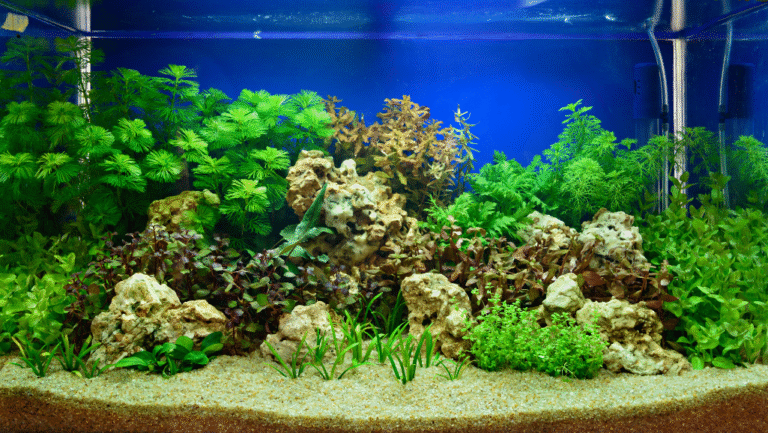
Neon tetras do best in aquariums that recreate their Amazonian home: soft, slightly acidic water, gentle currents, abundant plants and shaded areas. Getting the water parameters, tank layout, and filtration right gives your neon tetras the stable environment they need to thrive and display vivid color.
Essential Aquarium Setup for Neon Tetras
Start with the right tank size and equipment. A planted community aquarium of at least 10–20 gallons (≈40–75 L) is appropriate for a small school (6–10 fish); if you want more dramatic schooling behavior, choose a larger tank. Use a gentle, reliable filter (hang-on-back or canister with adjustable flow) to maintain water quality without creating a strong current that stresses these small fish. Provide plenty of mid-level swimming space and calm zones using driftwood, rock caves, and floating plants.
Water Parameters: Achieving the Ideal Conditions
Maintain stable parameters: temperature around 74–79°F (23–26°C), pH roughly 5.5–7.0 (slightly acidic to near-neutral), and soft to moderately soft hardness (GH ~1–8 dGH). Test your water regularly — frequent monitoring prevents sudden swings that can harm neon tetras. For breeding, slightly softer, more acidic water (pH near 5.0–6.0) and lower hardness are often used to mimic blackwater conditions.
Neon Tetra Tank Decorations and Plant Recommendations
Live plants improve water quality and comfort. Choose low- to medium-light species that tolerate soft water, such as Java Fern, Anubias, Cryptocoryne, Java Moss, and Amazon sword. Arrange dark substrate (fine sand or dark aquarium gravel) and add driftwood or leaf litter to release tannins and create a subdued, blackwater-like tone that helps neon colors pop. Keep lighting moderate to low—this reduces stress and mirrors their shady natural habitat.
Match decorations and plants with the needs of your species selections: understory plants and hiding spots benefit timid schooling fish and reduce aggression from more boisterous tankmates.
| Fish TypeCompatibility with Neon TetrasAverage Cost | ||
| Gold Neon Tetra | High | $2 – $3 |
| Long-finned Tetra | High | $2.50 |
| Diamond Neon Tetra | High | $3 |
Filtration, Flow, and Maintenance
Choose filtration that provides biological and mechanical filtration with gentle flow—sponge filters, hang-on-back units with flow controls, or canister filters with adjustable outputs work well. Aim for low to moderate water movement; neon tetras prefer calm midwater lanes. Perform regular maintenance: 20–30% weekly water changes (or as needed based on testing), vacuum the substrate lightly, and monitor ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, pH, and hardness using a reliable water test kit.
Checklist: Quick Setup Summary
- Tank: minimum 10–20 gallons (40–75 L) for a small school; larger for more fish.
- Temp: 74–79°F (23–26°C).
- pH: 5.5–7.0; breeding may require ~5.0–6.0.
- Hardness: soft to moderately soft (GH ~1–8 dGH).
- Filtration: biological + mechanical, gentle flow (sponge, HOB, or canister with flow control).
- Substrate & decor: dark substrate, driftwood/leaf litter, plenty of plants (Java Fern, Anubias, Crypts, Java Moss).
- Group size: 6+ neon tetras; 10+ preferred for natural schooling.
Following these setup and water parameters recommendations helps neon tetras stay healthy, reduces stress, and increases the likelihood of breeding in a planted home aquarium. For step-by-step product suggestions (filters, test kits, plant packages), consider a starter bundle linking tested equipment and plant lists to get your tank stable quickly.
Feeding Your Neon Tetra: A Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is one of the easiest ways to keep neon tetras healthy and colorful. These small omnivores do best on a mix of high-quality dry foods plus occasional live or frozen treats to supply protein, vitamins, and variety that support vibrant color and overall health.
Food Varieties and Nutritional Needs for Neon Tetras
Offer a base diet of quality flake or micro-pellets formulated for small tropical fish. Look for products with a good mix of protein and plant matter (many hobbyists use flakes or pellets with roughly 30–40% protein—avoid extremely high-protein specialist feeds meant for larger carnivores). Supplement the dry foods several times a week with live or frozen options such as brine shrimp, daphnia, microworms, and bloodworms to enhance color and vitality.
- Variety is key in the Neon Tetra diet—alternate flakes/pellets with live/frozen foods.
- Introduce live foods like brine shrimp and bloodworms periodically to boost color and natural foraging behavior.
- Include small amounts of plant matter (blanched spinach or crushed peas) occasionally for fiber.
Feeding Frequency and Portion Sizes
Feed small amounts 1–2 times per day or offer several very small feeds throughout the day. A useful rule: only provide what the school consumes within 2–3 minutes. Overfeeding leads to poor water quality, which directly harms neon tetras.
Practical portion guideline: for a small school (6–10 neon tetras), a pinch of flakes or a few micro-pellets per feeding is usually enough; adjust by observing how quickly the food is eaten. If uneaten food remains after 3 minutes, reduce the next feeding.
Tip: feed complete meals in short bursts—this reduces waste, stabilizes water parameters, and encourages natural schooling feeding behavior.
Supplements, Treats, and Food Preparation
Supplements are optional but can help recovery or coloration after illness. Use vitamin-enriched flakes or occasional immune-boosting supplements when recommended by a vet or experienced hobbyist. Treats like frozen daphnia or thawed brine shrimp are safe and attractive to neon tetras—thaw frozen foods in tank water and strain excess liquid to avoid contaminating the tank.
If you culture live foods (e.g., brine shrimp nauplii or microworms), ensure hygiene to prevent introducing parasites. Avoid feeding citrus fruits; small amounts of blanched peas are a safer plant-based treat.
Keeping feeding consistent and monitoring nitrate levels with a reliable test kit helps maintain a healthy environment. For supplies, check trusted sources for flakes, pellets, and live/frozen brine shrimp products.
Following these feeding guidelines will help your neon tetras maintain bright colors and stay active for years with proper overall care.
The Social Community: Choosing Compatible Tank Mates for Neon Tetras
Neon tetras are peaceful, visual schooling species that do best in calm community aquariums. When selecting tankmates, match water parameters (temperature, pH, hardness), temperament, and swimming level so all fish can thrive. Choosing non-aggressive, small-bodied companions helps neon tetras feel secure and reduces stress-related color loss or illness.
Consider the specific needs of potential tank mates neon candidates: some bottom-dwellers need fine substrate and hiding places; midwater swimmers require open lanes; and all should tolerate soft, slightly acidic water common for neon tetras.
Examples and general notes on common companions:
| SpeciesGroup SizeWater PreferenceCompatibility Note | |||
| Zebra Danios | At least 5 | Temperate to warm, pH 6.5–7.5 | Active but generally peaceful; can be more boisterous—monitor compatibility in smaller tanks |
| Harlequin Rasboras | 6 or more | Slightly acidic to neutral, 72–79°F | Peaceful, visually complementary; excellent midwater companions |
| Otocinclus Catfish | 3 to 5 | Soft, slightly acidic, similar temp | Great algae eaters; peaceful bottom dwellers that help keep the tank clean |
| Cherry Barbs | 5 to 6 (more females) | Slightly warmer, adaptable | Generally compatible if stocking favors more females to limit male aggression |
| Kuhli Loaches | 3–6 | Soft, slightly acidic | Nocturnal, peaceful bottom dwellers that won’t disturb midwater neon tetras |
Do / Don’t Checklist for Tankmate Selection
- Do choose small, peaceful, non-aggressive fish that share similar tank conditions (temp ~74–79°F / pH ~5.5–7.0).
- Do add companions in suitable group sizes—many community species are schooling themselves and appreciate company.
- Don’t add large or aggressive fish that may bully or eat neon tetras (cichlids, large barbs, aggressive gouramis).
- Don’t mix species with very different water parameter needs (e.g., very hard/alkaline water species).
Three Safe Community Layout Examples
- 10–20 gallon tank: 8–10 neon tetras + 3 Otocinclus + 1–2 kuhli loaches (plenty of plants and hiding spots).
- 20–40+ gallon planted tank: 12–15 neon tetras + 6 Harlequin Rasboras + 3 Corydoras (ample midwater and bottom structure).
- Larger community (40+ gallons): 20 neon tetras + small school of Celestial Pearl Danios or peaceful small rasboras + 4–6 shrimp or Otos for algae control (ensure shrimp compatibility and plenty of cover).
Other good companions sometimes recommended include Dwarf Gouramis (monitor for male aggression), Celestial Pearl Danios, and small peaceful catfish. Always research each species’ specific conditions (pH, temperature, diet) before adding them to the tank.
Choosing the right freshwater fish species and matching parameters ensures your neon tetras and their tankmates will thrive together. For an easy decision, try a compatibility chart or quiz to match species by temperament and water needs before you buy.
Conclusion
Caring for Neon Tetra is a rewarding mix of simple daily routines and attention to water chemistry and community dynamics. These colorful freshwater fish come from the Amazon Basin, where soft, tannin-rich waters and dense plant cover shape their behavior and needs. Recreating those stable conditions in your tank will keep neon tetras healthy, colorful, and active.
Quick Reference: Verified Care Parameters
| ParameterRecommended Range | |
| Temperature | 74–79°F (23–26°C) |
| pH | 5.5–7.0 (breeding often uses ~5.0–6.0) |
| Hardness (GH) | Soft to moderately soft: ~1–8 dGH |
| Tank size | Minimum 10–20 gallons (40–75 L) for a small school; larger preferred for visible schooling |
| Group size | 6+ (10+ recommended for best schooling) |
| Diet | High-quality flakes/pellets + occasional live/frozen brine shrimp, daphnia, bloodworms |
| Lifespan | Commonly 4–6 years in captivity; some may live longer with excellent care |
Signs of Illness & First-Aid Steps
Common issues include stress-related color loss, fin rot, ich, and bacterial infections (often grouped under “neon tetra disease” in hobbyist resources). Watch for faded color, clamped fins, lack of appetite, erratic swimming, or white spots. If you spot symptoms:
- Check water parameters immediately and perform a partial water change (20–30%).
- Quarantine sick fish when possible to prevent spread.
- Adjust temperature and maintain stable conditions; treat diagnosed diseases with targeted medication per label instructions.
- Address root causes: poor water quality, overcrowding, or incompatible tankmates.
Breeding Overview
Breeding neon tetras requires blackwater-like conditions: dim light, soft acidic water (pH ≈5.0–6.0), and fine-leaved plants or spawning mops. Use a separate breeding tank to protect eggs and fry; parents may eat their own eggs. Maintain very gentle filtration and keep water spotless during the spawning and rearing period.
Final Notes & Resources
Consistent care—stable water parameters, a balanced food plan, proper tank size, and suitable tank mates neon—is the key to healthy neon tetras. For a printable checklist (“Everything you need to know”) and a shopping bundle (test kit + recommended filter + plant list), consider linking to trusted suppliers and community guides.
Protecting their Amazonian home matters too: conservation of wild habitats helps sustain neon tetra populations and the ecosystems they depend on.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How do I properly care for Neon Tetras?
A: Maintain stable water (74–79°F / 23–26°C; pH 5.5–7.0), soft-to-moderate hardness, weekly partial water changes, gentle filtration, varied diet, and schools of 6+. Monitor water parameters regularly and avoid overcrowding.
Q: What does a Neon Tetra’s natural habitat look like?
A: They originate from shaded, tannin-stained streams and tributaries of the Amazon Basin (places in Colombia, Brazil, and Peru) with soft, slightly acidic water and heavy plant cover.
Q: Can you describe the typical behavior of Neon Tetras?
A: Neon tetras are peaceful, schooling tetras that prefer midwater lanes. They are shy but active in groups and rarely aggressive when kept with compatible species.
Q: What’s the lifespan of a Neon Tetra in captivity?
A: Expect 4–6 years on average with good care; exceptional individuals may live longer under ideal conditions.
Q: What is the ideal tank setup for Neon Tetras?
A: A planted 10–20+ gallon tank with dark substrate, driftwood/leaf litter for tannins, moderate lighting, gentle filtration, and room for schooling movement is ideal.
Q: How do breeding conditions differ for Neon Tetras?
A: Breeding uses softer, more acidic water (pH ~5.0), dim lighting, and a separate breeding tank to protect eggs and fry.
Q: What decorations are best for a Neon Tetra tank?
A: Live plants (Java Moss, Anubias, Java Fern, Cryptocoryne), driftwood, leaf litter, and smooth rocks—avoid sharp decor that can damage fins.
Q: What are the ideal diet and feeding guidelines for Neon Tetras?
A: Feed quality flakes or micro-pellets as a staple, supplement with brine shrimp, daphnia, or bloodworms occasionally, and provide small portions that are consumed within 2–3 minutes to prevent overfeeding.
Q: How should supplements and treats be used in a Neon Tetra’s diet?
A: Use fortified flakes or occasional vitamin supplements when recovering from illness or to enhance color; rely mostly on a balanced diet and fresh/frozen treats for variety.
Q: What are some compatible tank mates for Neon Tetras?
A: Compatible companions include small, peaceful species such as harlequin rasboras, otocinclus, corydoras, and other non-aggressive schooling fish—avoid large or aggressive species.