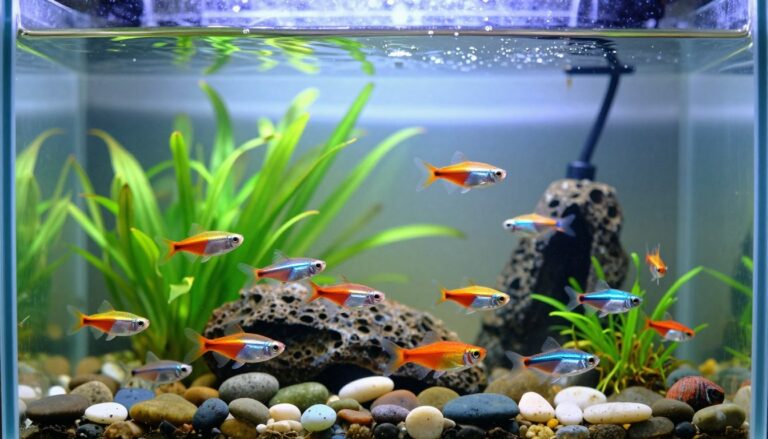
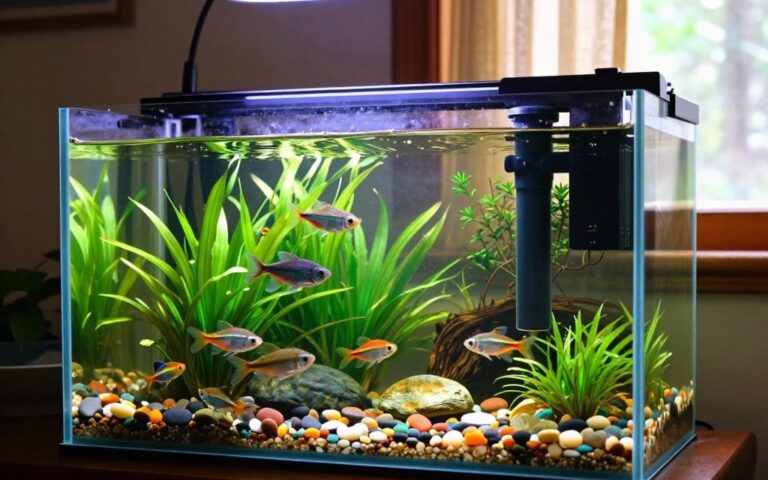
Welcome to the enchanting world of aquatics where aquarium fish tank with fish becomes a captivating hobby. It attracts new fans every year! Starting with setting up an aquarium fish tank is a journey filled with vivid imagery and tranquility. This beginner guide is here to help you learn how to care for fish in a tank, making your journey smooth and fun.
This guide is filled with detailed expertise, guiding you to a thriving freshwater home for your fish. We’ll explore the details of choosing the right tank, focusing on size, material, and compatibility with your fish. This sets the stage for a successful and sustainable underwater community.
Key Takeaways
- Selecting the correct tank size and material is crucial to accommodate specific fish species needs and ensure safety.
- Understanding the balance of lighting, temperature, and water conditions is imperative for a vibrant aquarium life.
- Essential equipment should include a reliable filtration system, appropriate lighting, and a stable heater to maintain optimal water conditions.
- Regular maintenance, including water changes and cleaning, promotes a healthy ecosystem for freshwater fish.
- With proper care, attention, and the right resources, anyone can build a serene aquatic sanctuary in the comfort of their home.
Essentials of Choosing Your Aquarium
Starting a freshwater fish aquarium means picking the best aquarium fish tank for your space and fish needs. The right tank size, material, and design are key for a healthy home for your fish. This helps keep your fish happy and healthy for a long time.
Finding the Ideal Size for Your Space and Stock
Choosing the right tank size is very important. It helps prevent overcrowding and keeps the water stable, especially in freshwater fish aquariums. Big tanks are better at keeping water conditions stable and give fish room to grow.
The rule is to have at least a gallon of water for every inch of fish. This ensures each fish has enough space. Also, knowing the recommended tank size helps prevent stress and disease in your fish.
Selecting the Right Material: Glass vs. Acrylic
Choosing between glass and acrylic tanks affects maintenance and how long the tank lasts. Glass tanks are popular for their scratch resistance and clear look. But, acrylic tanks are lighter and safer for homes with kids or in areas with stressors.
However, acrylic tanks need more care to avoid scratches. It’s important to handle them gently.
Understanding the Importance of Shape and Design
The tank’s shape is also crucial for your fish’s health. Rectangular tanks are best because they have a good surface area ratio. This helps with oxygen exchange and gives fish more room to swim.
While hexagonal or cylindrical tanks look nice, they might not be as good for gas exchange. This is important for keeping the water healthy in your freshwater fish aquarium tips.
In summary, picking the right aquarium tank is key for a successful and beautiful setup. Think about size, material, and design to meet your fish’s needs. This makes for a great and lasting hobby.
Setting Up the Perfect Underwater Habitat
Starting a fish tank setup is exciting as you build a lively freshwater aquarium. The aquarium’s success relies on careful planning and the right spot. Choose a place that supports the tank’s weight and keeps a stable temperature. Avoid areas with direct sunlight or heat sources to prevent algae and stress on fish.
The base of your aquarium is as important as its location. Make sure the stand can hold the tank’s full weight, which can be over 100 pounds for a 10-gallon tank. This is crucial, especially for bigger tanks that offer better water quality and more space but are heavier.
Adding beauty to your freshwater aquarium is important, but health comes first. Pick decorations that are safe and won’t change the water’s chemistry. Use clean substrates like gravel or sand and secure decorations to avoid accidents.
| Attribute | Recommendation | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Tank Size | 10 gallons or more | Better for water stability and more fish |
| Heating | 5 watts per gallon | Maintains tropical temperatures (74-80°F) |
| Filtration | Sponge filters | Simpler and easier for beginners |
| Lighting | LED solutions | Efficient and supports plant growth |
| Background | Dark colored, eco-friendly | Enhances visual depth, hides tubes/wires |
| Water Prep | Dechlorinator for tap water | Makes water safe for fish |
Creating a thriving freshwater aquarium is more than just filling a tank. It’s about building a balanced environment where fish can thrive. A well-thought-out setup with the right aquarium decoration ideas looks great and keeps your fish healthy.
Equipment Checklist for a Freshwater Fish Tank
Starting a thriving fish tank begins with the right equipment. Each piece, from filters to lighting, is key to a healthy tank. Here, we list the must-haves for a well-running tank, perfect for your fish and plants.
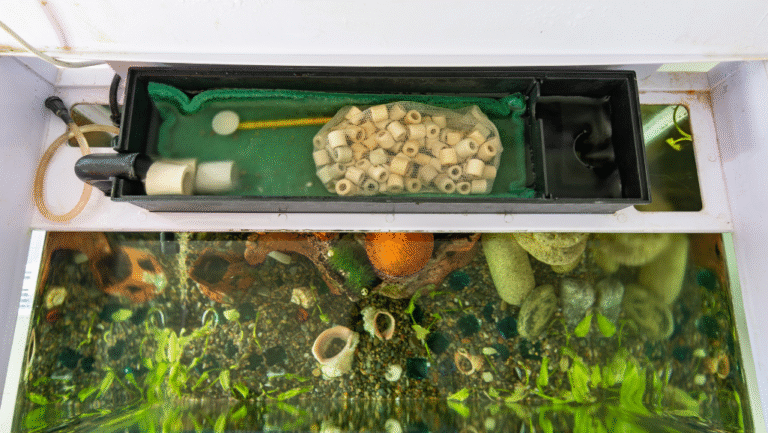
Filtration Systems: Types and Recommendations
Choosing the right filter is crucial for aquarium fish care. Filters keep the water clean by removing waste and toxins. For small tanks, an internal filter works well. But, bigger tanks need a strong external or canister filter.
Think about the size and type of fish you have. This will help you pick the best filter for your tank.
Heaters and Thermometers: Creating a Stable Environment
Tropical fish like temperatures between 74-80°F. So, a good heater and thermometer are a must. Pick a heater that gives about 5 watts per gallon of water. This keeps your tank at the right temperature.
It’s better to choose a heater that’s a bit stronger than needed. This way, you’re ready for any temperature changes.
Lighting Necessities for Fish and Plant Health
Good lighting is key for seeing your fish and keeping plants healthy. LED lights are best because they’re efficient and mimic natural light. They help plants grow and keep fish healthy.
LED lights with timers make it easy to keep a day and night cycle. This is a big part of aquarium maintenance tips.
| Accessory | Use | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration System | To maintain water quality by removing toxins and waste | Size-dependent: Internal for small, Canister for large tanks |
| Heaters | To stabilize water temperature for tropical fish | Approx. 5 watts per gallon of water, choose next size up for safety |
| LED Lighting | For plant growth and natural light cycles | Energy-efficient LEDs with a timer |
Having the best fish tank accessories makes life better for your fish and plants. It also makes aquarium maintenance easier. Think about your tank’s needs and choose wisely to create a healthy home for your aquatic friends.
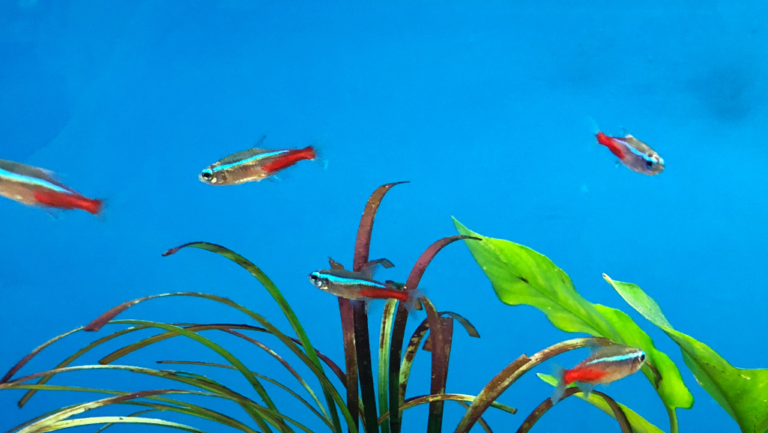
Aquarium Fish Tank with Fish: Stocking Guidelines
Starting a vibrant and healthy aquarium begins with knowing the right stocking guidelines. Choosing the right popular fish for aquariums is key. It’s important to ensure each fish has enough space and resources to live well.
How to Choose Compatible Fish Species
Choosing aquarium fish species that get along is crucial. A common rule is one inch of fish per one gallon of water. But, bigger fish like goldfish need more space, about one inch per two gallons. This helps prevent overcrowding and improves their quality of life.
Adding Plants to Your Freshwater Ecosystem
Adding plants like Java Fern, Anubias, and Vallisneria makes your tank look great. They also help keep the ecosystem balanced. Plants add oxygen, provide hiding spots, and control nutrient levels, which is good for a healthy fish tank.
Introducing New Fish: Acclimation Tips
Introducing new fish slowly is important to avoid stress. Never add more than 25% of the tank’s capacity at once. Slowly getting the fish used to the tank’s water temperature and chemistry helps them stay healthy.
| Aquarium Size (Gallons) | Recommended Stocking (One Inch Fish per Gallon) | Surface Area Rule (Square Inches) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 gallons | Not advisable for heavy stocking | 120 square inches |
| 25 gallons | Varies by the fish type | 300 square inches |
| 50 gallons | Common sense approximations | 600 square inches |
| 100 gallons | Based on volume of fish | 1200 square inches |
The size of your tank and the fish in it should match these guidelines. This ensures a healthy and lively fish tank. A bit of planning is all it takes to keep your fish happy and healthy.
Maintaining Your Aquatic Ecosystem for Longevity
To keep your aquatic environment healthy, following fish tank maintenance tips is key. Regular water changes, monitoring water quality, and cleaning are essential. These steps help keep your freshwater fish happy and healthy.
Regular Water Changes and Water Quality
Water changes are vital for freshwater fish tank maintenance. Experts suggest changing 15-25% of the water every two to four weeks. This keeps the water quality high and removes harmful substances.
Testing water parameters like pH and ammonia is also crucial. It helps catch any imbalances early, keeping your fish safe.
Disease Prevention and Health Monitoring
Good fish tank care means watching your fish for signs of stress or illness. Catching health problems early can stop outbreaks. This is especially important in a closed space like an aquarium.
Preventive steps like quarantining new fish and checking their behavior are key. They help keep your tank disease-free.
Cleaning Techniques for a Pristine Aquarium
Cleaning is essential for your aquarium’s look and health. Regularly removing algae and vacuuming the substrate keeps the tank clear. Also, maintaining the filtration system is vital for clean water.
Remember to replace filter media and trim plants carefully. This avoids overgrowth and waste in the tank.
| Maintenance Activity | Frequency | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Water Changes | Bi-weekly to Monthly | Removes toxins and replenishes nutrients |
| Water Quality Testing | Weekly | Early detection of imbalances |
| Filtration System Maintenance | Monthly | Ensures optimal water filtration |
| Algae Removal | As needed | Keeps tank walls clear and clean |
| Plant Trimming | Monthly | Prevents crowding and promotes growth |
| Fish Health Monitoring | Daily to Weekly | Prevents disease and stress in fish |
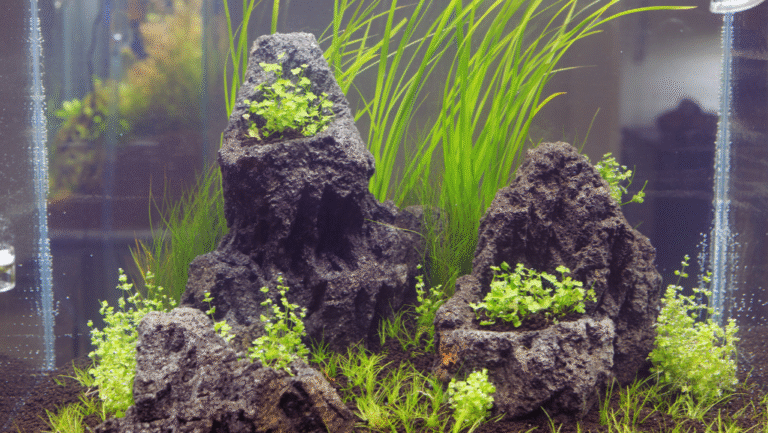
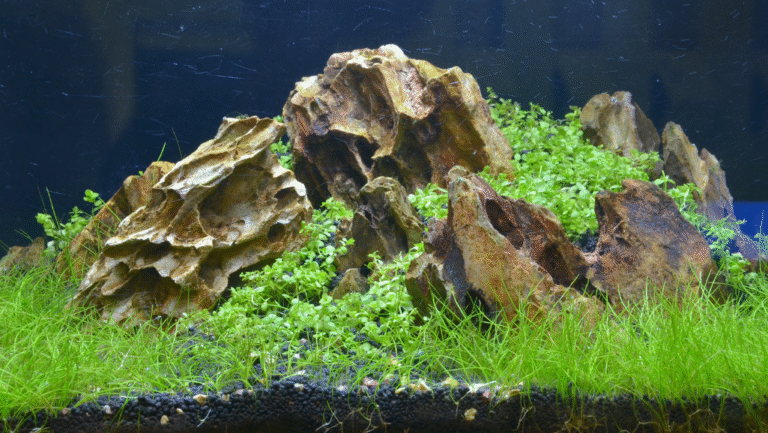
The Art of Aquarium Decoration and Aquascaping
Adding an aquarium to your home can turn a simple room into a peaceful oasis. The art of aquascaping is about creating a beautiful underwater world. It supports the health of fish and plants. Start by picking the right aquarium decorations that fit your style and your fish’s needs.
Start with substrates like sand or gravel. Then add driftwood and rocks for hiding spots. These elements are not just pretty; they also help your fish feel safe and healthy.
There are many aquascaping styles to choose from, like Nature Aquarium and Dutch. Each style has its own look and challenges. Adding LED lights and good filtration helps plants grow and keeps the water clear.
| Item | Price | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Pure Iconic Black Pearl Shrimp KIT 7.13 Gallon | $199.49 | Includes tank and specialized equipment for shrimp keeping. |
| Mr Aqua Pure 7.13 Gallon Cube Aquarium Kit | $129.99 | Compact and clear cube design for small aquascapes. |
| Mesh DIY Aquarium Lid Kit B | $41.99 | Customizable lid for tanks up to 45 x 45 cm. |
| Tranquility Iconic 95 gal. LI Aquarium | $943.95 | Large installation piece for expansive aquascapes. |
Mastering aquascaping techniques means placing elements carefully. Use the Rule of Thirds and Golden Ratio for a balanced look. This makes your aquarium a beautiful and peaceful place.
Start your aquascaping journey by choosing decorations and designs. Whether you prefer a Nature Aquarium or Iwagumi, each step makes your aquarium a living art piece. It brings joy to you and your fish.
Understanding the Nitrogen Cycle and Biological Filtration
Learning how to cycle a fish tank is key for new aquarists. The nitrogen cycle is vital. It turns harmful substances into safer ones.
The cycle starts with organic matter breaking down. This creates ammonia, which is toxic to fish. Then, beneficial bacteria turn ammonia into nitrites and nitrates. These are less harmful and easier to manage with regular care, as shown in this freshwater aquarium guide.
The Role of Beneficial Bacteria in Your Fish Tank
Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter bacteria are crucial. They live on surfaces and in filter media. They convert ammonia and nitrite into nitrate.
Building a strong bacteria colony is essential. It can take one to six weeks. Keeping the aquarium water temperature for fish right helps them grow.
Strategies for Managing Ammonia, Nitrite, and Nitrate
It’s important to keep nitrogen levels in check. Regular water tests and changes are key. This helps avoid toxicity risks to fish.
Using a big biofilter and biological media like MarinePure® helps. They offer more space for bacteria to grow. This stabilizes the water chemistry.
| Component | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Ammonia | Produced by decaying fish waste and uneaten food | Highly toxic, requires immediate conversion |
| Nitrites | Intermediate product in nitrogen cycle | Toxic, binds with hemoglobin in fish |
| Nitrates | Final product of the nitrogen cycle | Less harmful; managed by water changes and plant absorption |
Using these tips in your freshwater aquarium guide will help your fish stay healthy. It shows how important it is to understand and manage the nitrogen cycle.
Buying Guide: Where to Find the Best Aquarium Supplies Online
Setting up your aquarium needs high-quality equipment and accessories. This ensures your aquatic environment is safe and appealing. Shopping online to buy aquarium fish tank is convenient and offers a wide variety. But, it’s important to know where to look.
For beginners, finding reliable platforms is key to setting up a successful aquarium. We’ll explore different options and guide you to make the best choices for a thriving aquatic habitat.
Comparing Prices and Customer Reviews
Price and customer experiences are important when choosing where to buy aquarium supplies. Online retailers often share customer feedback. This helps you judge the quality of the tank and the health of the best fish for aquarium. LiveAquaria is a reliable source, offering detailed information and reviews on various products.
Accessories and Kits for Beginners
Newcomers might start with a 20-gallon tank. It’s more resilient to changes and easier to manage. You’ll need submersible heaters for tropical fish and power filters for clean water. Kits from LiveAquaria include everything you need, making setup easier.
Choosing the right store means considering variety and quality. Local stores let you see products in person, but online stores offer more options at lower prices. Remember, starting with the right equipment is as important as choosing the right fish and a proper maintenance schedule.
Conclusion
Starting a fish tank hobby can be very rewarding. It brings color and life to your home and connects you with the underwater world. This guide covered the basics of setting up and caring for your tank, including essential accessories and water care tips.
Studies show that keeping an aquarium can help reduce stress. But, it’s crucial to make smart choices to keep your fish healthy and happy.
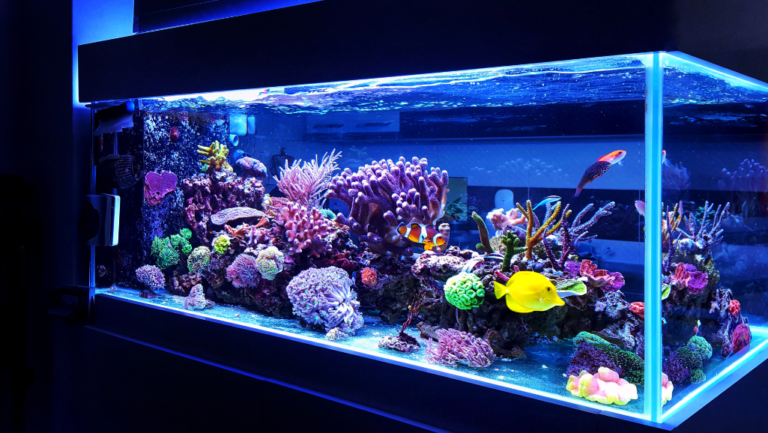
Choosing the right aquarium is key. You can pick from simple freshwater tanks or complex marine setups. Each has its own needs and challenges. Freshwater tanks are easier and cheaper, making them great for beginners or those who want a peaceful space.
Creating a marine aquarium is more complex but rewarding. It requires careful planning and attention to detail. Your daily efforts will make your tank a thriving, beautiful space.
Using the right supplies from online retailers is important. It ensures your tank is not only beautiful but also healthy. With patience and care, your tank will become a living art piece that benefits everyone involved.