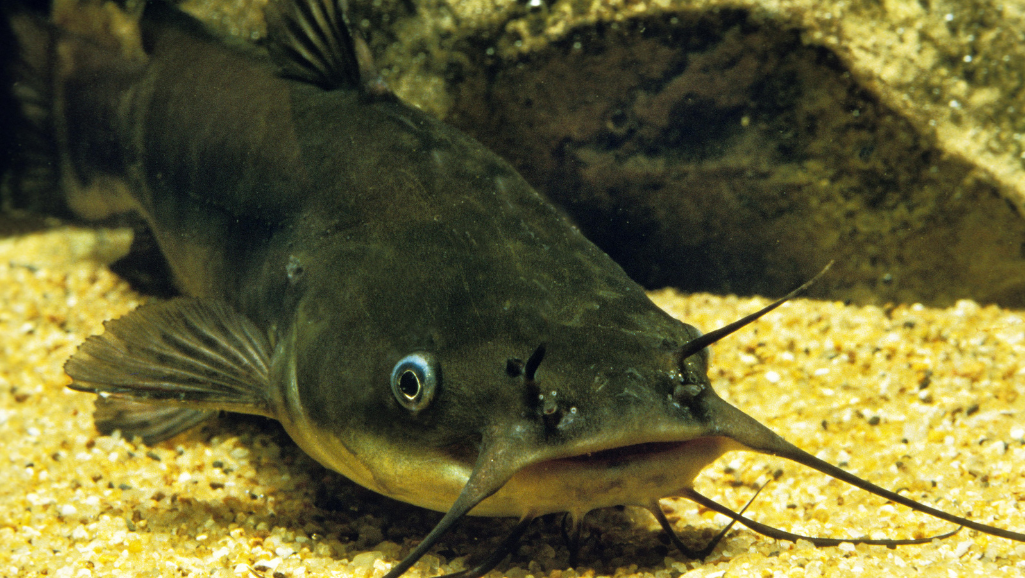
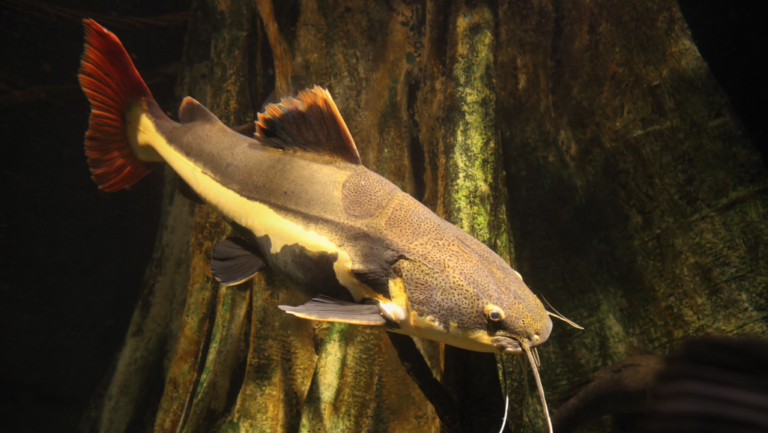
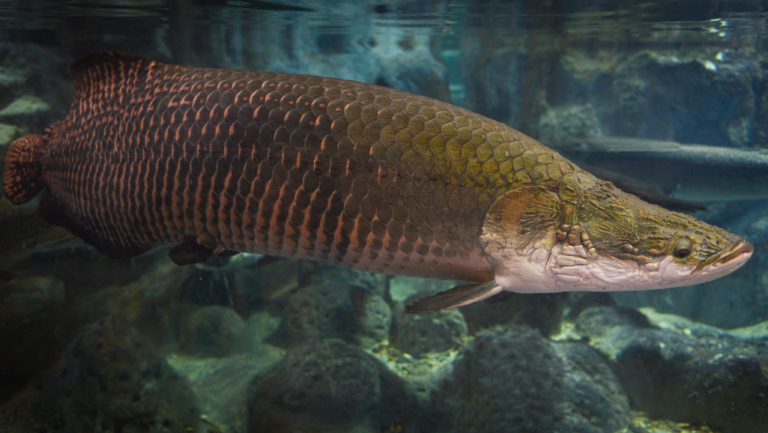
In the world’s rivers, the vulture catfish is a mysterious creature. Brazilians call it the ‘water vulture’ because of its scavenging ways. It’s a necrophagous fish, eating the dead that others ignore.
Despite its role in the ecosystem, it has a bad reputation. This is because of seafood fraud and illegal fishing. In Manaus, Brazil, the names ‘douradinha’, ‘douradinho’, and ‘piratinga’ often hide the truth about C. macropterus in markets.
This deceit harms both people and marine life. It’s important to know the truth about this fish. Research has shown how common seafood fraud is, including with vulture catfish.
This knowledge is critical for protecting both humans and the ocean. We need to identify and conserve this species accurately.
Key Takeaways
- The vulture catfish, scientifically known as C. macropterus, demonstrates unique scavenging behavior in aquatic ecosystems.
- Brazilians colloquially refer to this catfish species as ‘water vulture’ due to its necrophagous diet.
- Seafood fraud in markets often hides the identity of the vulture catfish under various names.
- Oceana’s report has shed light on global seafood mislabeling, with a concerning incidence of misrepresented vulture catfish.
- The conservation of vulture catfish is imperative due to the ecological role they play and the threat of mercury exposure that has led to fishing restrictions.
- Researchers are working on innovative DNA analysis methods to combat seafood fraud and protect the integrity of marine biodiversity.
Introduction to Vulture Catfish
Exploring the Vulture Catfish, known as C. macropterus, reveals a fascinating aquatic creature. It is known for its scavenging skills. Found mainly in the Amazon basin, it is a key part of its ecosystem, earning the nickname ‘water vulture’ for its cleaning role.
Overview of the Species
Learning about Vulture Catfish care starts with their physical and behavioral traits. They can grow up to 60cm in the wild but stay around 40 to 50cm in tanks. Despite their scary name, they are social, enjoying body contacts and group activities. Knowing vulture catfish facts is vital for those thinking of keeping them as pets.
Habitat and Range
The Vulture Catfish calls the northern South America home, mainly in the Amazon river systems. Their habitat is key to their growth, affecting their scavenging and social behaviors. To care for them in tanks, you need a space that mimics their natural home. This means a tank of at least two meters long, filled with stones and plants to look like a river.
Vulture Catfish can thrive in captivity if their size and social needs are met. They should be kept with fish of similar size to prevent fights. Knowing how to care for them is essential for creating a healthy, lively aquatic home.
Unique Characteristics of Vulture Catfish
The Vulture Catfish is a unique fish found in the Amazon and Orinoco basins. It has vulture catfish size up to 40 centimeters. This makes it a big fish in its home waters.
Physical Features
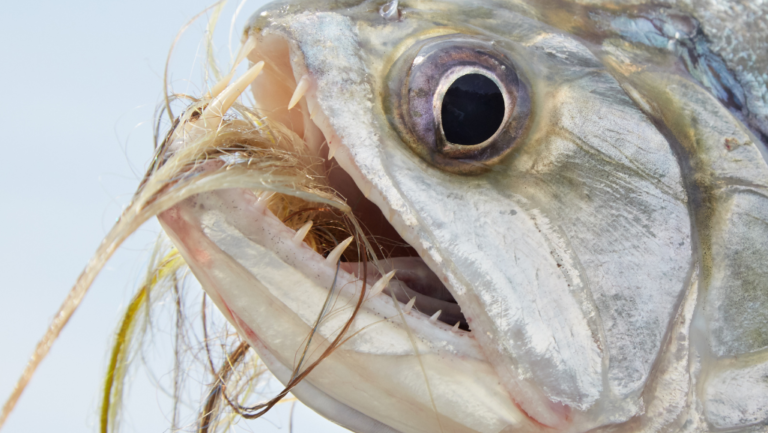
This fish has a small mouth but a strong bite. It can eat a lot of food quickly. Its body is built for swimming fast in the water.
Sensory Abilities
The Vulture Catfish has special senses. It can feel changes in water chemistry. This helps it find food in dark waters.
Knowing about aggressive fish like the Vulture is key. They need careful tank mates to avoid fights.
For more on keeping Vulture Catfish, check out vulture catfish behavior and care. They are interesting and need special care.
Ecological Role in Freshwater Ecosystems
The vulture catfish is key to keeping freshwater ecosystems balanced. It eats dead fish and organic waste, helping to recycle nutrients. This keeps the water clear and healthy. Knowing about their size and scavenging habits shows their big role in the water.
Scavenging Behavior
Vulture catfish mainly eat carrion and detritus, using their sharp senses to find it. This helps keep their homes clean by stopping the buildup of rotting matter. Their size lets them eat big pieces, making them great at cleaning polluted water.
Impact on Water Quality
Vulture catfish do more than just clean. They help keep oxygen levels up for other fish and creatures. Their size also lets them mix up sediment, bringing up nutrients that help the ecosystem thrive.
In short, vulture catfish help keep water quality high by eating waste. They make their ecosystems healthier and more stable. This shows why we need to protect these important species.
Diet and Feeding Habits of Vulture Catfish
The Vulture Catfish, known scientifically as Calophysus macropterus, has unique eating habits. These habits are key to keeping their freshwater homes healthy. Knowing how to feed them is important for those who keep them in aquariums.
Types of Food Consumed
Vulture Catfish mainly eat dead and rotting fish and other sea creatures. This makes them look like ‘water vultures’ to people who live nearby. They also eat small bugs and plants, playing a big part in cleaning their homes.
Feeding Techniques
How Vulture Catfish eat is just as interesting as what they eat. They have special feelers around their mouths to find food in dark waters. When they find something, they suck it in to clean the water.
Looking after these catfish means making their food and home like their natural one. This includes giving them different foods and keeping their water clean and right for them.
In summary, what Vulture Catfish eat and how they eat is very important. It helps them live and keeps their home healthy. People who keep them in tanks should try to make their home as natural as possible.
Conservation Status and Threats
The vulture catfish is key to keeping freshwater ecosystems healthy. It helps clean up dead plants and animals in water. We must protect it to keep our waterways balanced.
Unfortunately, their numbers are dropping fast because of humans. These catfish are not just studied but also sold in markets. This has led to a big demand for vulture catfish for sale. We’ll look at the main dangers and what’s being done to save them.
Major Threats to Population
- Habitat Loss: Big deforestation and dam building harm their homes.
- Fishing Pressure: They get caught by accident in fishing nets.
- Environmental Pollution: Pollution from factories makes their homes worse.
- Seafood Fraud: Wrongly labeled seafood makes saving them harder.
Conservation Efforts
To save the vulture catfish, we need good plans. Some places have stopped fishing to help them grow back. Groups and agencies are using DNA tests to stop illegal fishing and make rules stricter.
- Protected Areas: Safe zones are set up to protect their homes.
- Regulatory Reforms: New fishing rules and checks are put in place.
- Community Education: Teaching locals about these fish and why they matter.
- Research and Monitoring: Studies help us understand and protect them better.
Keeping vulture catfish safe is vital for our water’s health. With more work, we hope to save this important species. Governments, experts, and local people must work together for their future.
Fascinating Facts About Vulture Catfish
The Vulture Catfish, known as Calophysus macropterus, is misunderstood. People often see them as just scavengers. But they are vital to their ecosystems, much like vultures in the sky.
They feed on bones and dead animals. This helps keep their habitats healthy. Their diet is unique and important for their environment.
Myths and Misconceptions
Many think Vulture Catfish are just scavengers. But they are more than that. In Brazil, they are sold under nicer names to avoid the scavenger label.
They grow fast in good conditions. Young ones can grow twice as long in a year. This shows how adaptable they are.
Cultural Significance in Various Regions
Vulture Catfish have a big impact beyond their role in the ecosystem. They show how local diets and markets are connected. They are found mainly in South America.
Like vultures, they play a key role in their ecosystems. Their behavior is similar to that of migratory birds. They are part of a bigger story about biodiversity and balance.
Learning about Vulture Catfish is more than just facts. It’s about understanding their role in keeping waterways healthy. It also shows respect for the cultures that eat them. Just like Tiger Oscars, they show us the beauty of aquatic life and the need for care.
By knowing more about these aquatic scavengers, we can appreciate them more. It encourages us to take better care of fish and our planet.