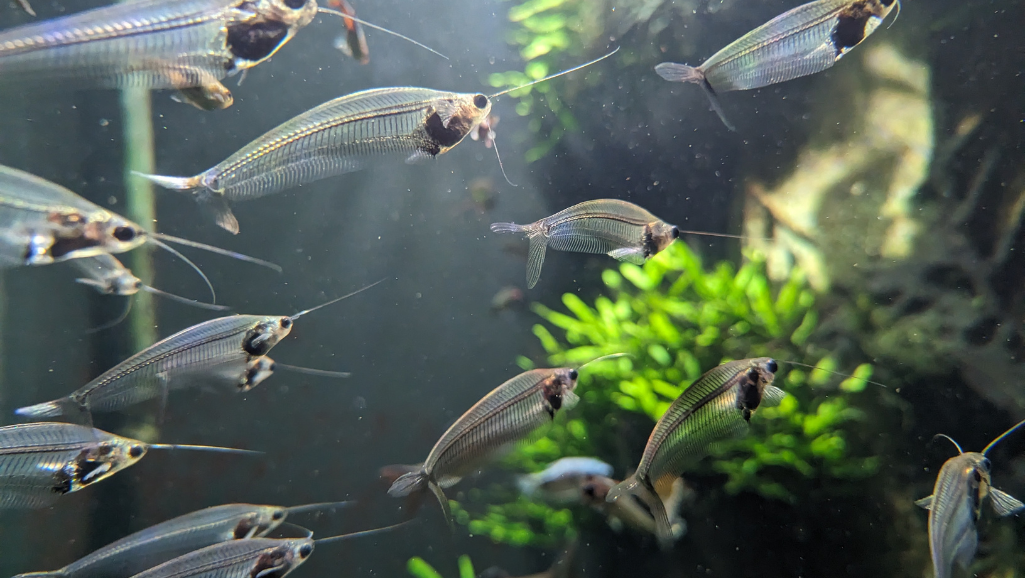
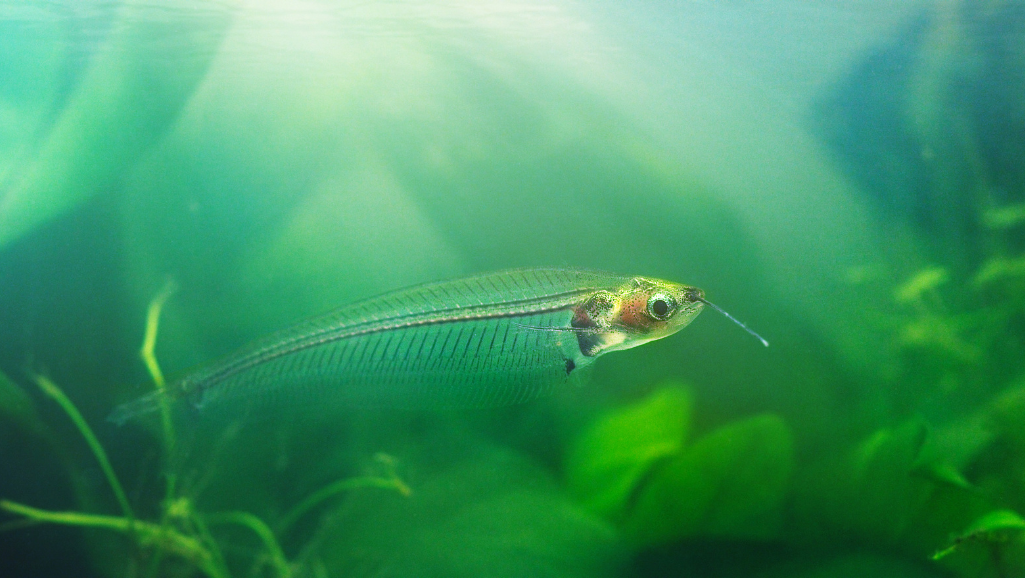
Watch a schooling glass catfish display and you get a living light show — welcome to practical Glass Catfish Care. Translucent bodies glide in midwater, adding calm motion to planted community tanks. These peaceful catfish originate in Southeast Asia and respond best to steady routines rather than dramatic changes; with consistent care many live around 7–8 years.
Read on to learn the essentials: recommended tank size, stable water parameters, aquascape tips, feeding and diet, compatible tankmates, common health issues, and rare breeding notes. Aim for at least a 30-gallon aquarium with gentle flow and soft, slightly acidic water near 76°F to recreate their natural environment and encourage schooling.
They thrive in groups. Plan for a small school to boost confidence and unlock natural schooling behavior. These mostly scaleless fish need careful acclimation and steady water conditions to avoid ich and stress. A varied diet of quality micro flakes or pellets plus frozen or live foods builds robust immunity and supports long-term health.
Key Takeaways
- Translucent midwater schooling creates a serene focal point in community tanks.
- Provide a 30+ gallon aquarium with soft, slightly acidic water and stable temperature.
- Keep them in groups and use live plants, driftwood, and subdued light for the best display.
- Feed a varied diet — micro flakes/pellets plus frozen or live brine shrimp and daphnia — to maintain condition.
- Scaleless species are sensitive to parameter swings; routine testing and gentle maintenance prevent most problems.
Meet the Glass Catfish: What Makes These “Ghosts” So Mesmerizing
Understanding which species you own changes how you provide Glass Catfish Care. A mislabeled store tag can change the tank size, diet, and social needs your fish require, so learning basic ID and anatomy helps you give the right environment and husbandry.
True identity: vitreolus vs. kryptopterus bicirrhis
“Before 2013 most hobby specimens were mislabeled; careful research showed the common aquarium species is K. vitreolus.”
Most fish sold as “glass catfish” are actually Kryptopterus vitreolus. K. vitreolus is the smaller, more transparent kind commonly seen in the hobby (adult length ≈3 inches). The historically cited K. bicirrhis is a different species — reaching roughly 6 inches — that is less glasslike and often more assertive. A rarely traded dwarf form, K. minor, is reported only occasionally in specialist collections.
Transparency explained: anatomy and hidden fin
The genus Kryptopterus gets its name from the reduced dorsal — literally “hidden fin” — which contributes to the ghostly silhouette hobbyists prize. Truly clear bodies let you observe the spine, eyes, and a silvery organ sack behind the head; after a large meal the digestive tract may be visible, offering a live anatomy lesson in your aquarium.
- Most aquarium specimens are K. vitreolus (≈3 inches, peaceful schooling behavior).
- K. bicirrhis grows to ~6 inches, appears semi-opaque, and can be bolder than vitreolus.
- Transparency is a natural trait of these species — it is not caused by dyes or water treatments.
Quick ID checklist when buying: check adult size listed by the seller, note dorsal fin visibility (reduced in Kryptopterus), observe how transparent the body is, and ask about the wild-capture or captive-bred source. For deeper reading and species notes, consult reliable references such as the species profile linked in the original article (this practical reference) and museum or taxonomic papers that discuss the 2013 clarification of vitreolus identity.
Glass Catfish
Native southeast asia streams shape how these glass catfish behave and how you should set up their tank to mirror that environment.
Native habitats and schooling behavior
K. vitreolus commonly enters the trade via Thailand and is associated with slow-moving, shaded streams and tributaries where soft, slightly acidic water collects among leaf litter, dense aquatic plants, and fallen wood. These tannin-stained waters provide cover and abundant microcrustaceans.
In the wild glass catfish often form large schools — from dozens up to hundreds — sweeping from cover into open swim lanes to feed on tiny crustaceans and insect larvae. That schooling instinct is why you’ll see far better, bolder behavior when you keep a proper group in the aquarium.
They are true midwater swimmers (not bottom dwellers), so design your tank with clear midwater corridors and shaded planting. A steady water temperature near 76°F closely matches their native range and helps maintain regular feeding and activity.
- Anchor tank design to shaded-stream aesthetics and plant-rich margins.
- Create both covered areas and open swim corridors to reflect wild flow and encourage schooling.
- Maintain a healthy group size so the school displays natural synchronized movement.
Typical natural-habitat parameters to emulate: pH slightly acidic (often in the high 5s to low 7s), soft to moderately soft water, and stable temperatures in the mid-70s°F. For more on wild range and species notes, see the K. vitreolus profile linked in the original article: K. vitreolus.
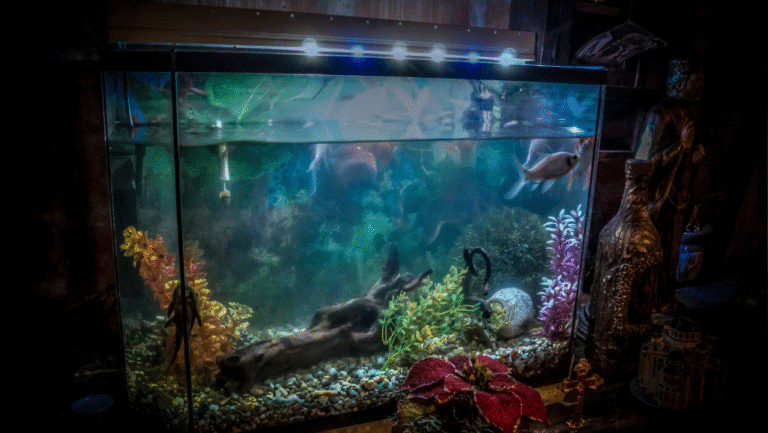
Setting Up the Ideal Glass Catfish Tank
Creating roomy swim corridors and shaded cover is the first step to calm, confident schooling — the core of good Glass Catfish Care. Design your aquarium to echo slow tropical streams so shy swimmers feel safe and display naturally.
Tank size and layout that encourage schooling
Start with at least a 30-gallon tank to provide stable conditions and real midwater space for a small school. A wider footprint is preferable to extra height — glass catfish need horizontal swim lanes. Frame open corridors with dense planting and branching driftwood to create both sheltered edges and showy midwater lanes.
Target water parameters (quick reference)
- Temperature: mid-70s°F (aim for ~76°F; comfortable range ~74–80°F)
- pH: slightly acidic to neutral (high 5s up to ~7.0)
- Hardness: soft water is ideal (roughly 0–6 dKH)
- Flow: gentle to moderate, mimicking sheltered stream currents
These water parameters reduce stress and encourage steady activity in the school. Regular testing keeps conditions predictable; consistency matters more than exact numbers.
Filtration, flow, and equipment tips
Use a powerhead-equipped hang-on-back, canister, or sponge filter with adjustable output so you can dial in gentle flow. Aim for good surface exchange and oxygenation but avoid strong jets that create chaotic currents — glass catfish prefer smooth, laminar flow that guides them through midwater corridors.
Equipment examples: a canister filter with a spraybar or a power filter with a flow diffuser gives control over current; add a sponge pre-filter or gentle flow attachment if your filter is strong. For planted community tanks, an inline heater or quality submersible heater maintains steady water temperature.
Lighting, aquascape, and substrate
Choose subdued lighting to reduce stress and accentuate translucence. Use driftwood, leaf litter, or Indian almond leaves to introduce tannins and gentle shade — these materials mimic the fish’s natural habitat and calm skittish animals.
- Substrate: smooth sand or very fine gravel protects delicate barbels and supports rooted plants.
- Plants: dense midground and background plants (crypts, java fern, anubias, vallisneria) create cover and visual barriers.
- Decor: multiple root/wood hideouts let schools retreat and reset after disturbances; keep midwater lanes free of clutter for display.
Stocking and community tanks
Plan tankmates that share midwater habits and peaceful temperaments. Avoid boisterous or nippy species that chase or stress the school. When planning stocking levels, remember that glass catfish are schooling fish — larger groups produce better behavior and are less stressed.
Practical notes: precondition new water before changes (match temperature and chemistry), and cycle filters fully before adding glass catfish to keep beneficial bacteria intact. Stability and gradual adjustments protect these sensitive, mostly scaleless fish.
Summary: choose a 30+ gallon aquarium with a broad footprint, soft slightly acidic water, subdued lighting, tannin-rich cover, smooth substrate, and a filter setup that provides gentle, adjustable flow — together these choices create the ideal conditions for healthy, confident schooling glass catfish.
Daily Care Routines: Water Quality, Stability, and Monitoring
Daily checks and gentle maintenance build the consistent conditions glass catfish need to thrive. Create a short, repeatable routine you can follow each day so the school experiences minimal stress and long-term health.
Quick maintenance checklist (Daily / Weekly / Monthly)
- Daily: glance at fish behavior (swimming in midwater, eating normally), check heater/readout for steady temperature, and remove visible debris or uneaten food.
- Weekly: test key water parameters — ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, pH, and general hardness — and perform a 10–25% partial water change depending on stocking and nitrate levels.
- Monthly: rinse mechanical filter media in tank water (not tap water) to preserve beneficial bacteria, inspect equipment, and review your maintenance log for trends.
What to test and why
Focus on the basics: ammonia and nitrite must be zero; nitrate should stay low (<20–40 ppm depending on stocking). pH and hardness influence physiology — glass catfish prefer soft, slightly acidic to neutral water — so monitor these values regularly to avoid sudden swings that stress scaleless fish.
Acclimation and quarantine
Acclimate new arrivals slowly using a drip or bucket method to match temperature and chemistry. Quarantine every new fish in a separate aquarium for observation (two weeks is a common minimum) to prevent parasites and diseases from entering your display tank.
Practical tips to keep water stable
- Use preconditioned water for changes (match temperature and pH as closely as possible).
- Keep a written log or spreadsheet of readings and water changes — trends reveal problems earlier than isolated checks.
- Feed small amounts and remove uneaten food promptly to reduce nitrate buildup.
- When cleaning filters, avoid sterilizing media; preserve beneficial bacteria by rinsing in removed tank water.
“Small, steady steps in maintenance save time and heartache later.”
Recommended test kits and timing
Choose reliable test kits (liquid titration kits or high-quality strips) for ammonia/nitrite/nitrate/pH and consider a GH/KH test for hardness. Test weekly as a baseline and more often if you see behavior changes (clamped fins, hiding, or sudden darting), which often indicate chemistry or temperature issues.
When to act
If ammonia or nitrite appears above zero, perform an immediate partial water change and check filtration. If nitrates climb, increase the frequency or volume of water changes. For unexplained stress or disease signs, isolate affected fish in quarantine and consult experienced hobbyists or an aquatic veterinarian before applying medications — glass catfish are sensitive and benefit from gentle treatments.
Feeding Your Glass Catfish for Health and Longevity
Match feeding to their natural prey and you’ll see steady growth, better coloration, and livelier schooling behavior. In the wild glass catfish consume zooplankton, tiny crustaceans, and insect larvae — so in captivity prioritize small, protein-rich foods that mimic that profile.
Natural diet vs. aquarium substitutes
Focus on fine prey analogs. Use high-quality micro flakes or micro pellets as the daily staple. Supplement regularly with frozen or live brine shrimp and daphnia, and offer bloodworms occasionally for variety and conditioning.
Feeding frequency, portions, and a sample schedule
Feed small amounts 2 times per day as a baseline; during conditioning or growth periods increase to 3 light meals. Portions should be bite-sized and consumed within 1–2 minutes to protect water quality — these fish have tiny mouths and are inefficient competitors if kept alone.
- Sample schedule: morning — micro flakes/pellets (1–2 pinches for the school); midday — a small serving of frozen daphnia or enriched brine shrimp; evening — a light flake/pellet feed or occasional live food.
- Target-feeding: gently drop frozen or live foods into the midwater schooling zone rather than at the surface so shy individuals can access food. Use a feeding ring or a long-tongued pipette to place food precisely if competition is an issue.
- Rotate textures: alternate pellet, frozen, and live offerings to maintain appetite and digestive health.
- Enrichment: soak frozen foods briefly in a vitamin or omega-rich supplement to boost nutrition, especially during seasonal changes or recovery from illness.
Practical alternatives and product tips
If live foods are hard to source, high-quality frozen brine shrimp and frozen daphnia are excellent substitutes — thaw and rinse to remove excess preservative solution. Look for micro pellets formulated for small omnivores; brands that emphasize high protein and small pellet size work best. For flakes, choose a micro-flake that lists protein sources high on the label.
Troubleshooting feeding problems
- Refusal to eat: try warming frozen foods slightly, offering live daphnia, or temporarily darkening the tank to reduce stress at feeding time.
- Bullying at feed time: add more dispersed feeding points or use target feeding to ensure shy fish get food.
- Water quality decline after feeding: reduce portion sizes, feed less frequently, or perform a partial water change after heavy feeding sessions.
“Consistency in feeding builds boldness and keeps condition steady.”
By matching food size and frequency to natural preferences — micro flakes/pellets plus routine offerings of brine shrimp, daphnia, and occasional bloodworms — you support long-term health and encourage confident, synchronized schooling in your glass catfish.
Choosing Peaceful Tankmates and Building a Harmonious School
A confident school begins with the right numbers and gentle neighbors in the aquarium. Commit to a proper group size first, then add calm companions that share midwater habits and similar water parameter requirements.
How many to keep: Keep at least six glass catfish to unlock authentic schooling behavior; groups of 8–12 are better if your tank size allows, because larger schools increase confidence and produce more synchronized movement.
Compatible companions (Do)
Choose peaceful, small-bodied midwater swimmers or gentle bottom-dwellers that won’t harass the school. Good options for community tanks with similar conditions include ember tetras, harlequin rasboras, small Corydoras species, and honey gouramis (the peaceful varieties).
Species to avoid (Don’t)
Avoid boisterous, nippy, or large fish that chase midwater swimmers — examples include large barbs, many cichlids, and larger or aggressive gouramis. These species stress glass catfish and disrupt schooling display.
“The harmony of the group is the heartbeat of a successful display tank.”
Stocking examples by tank size
- 30-gallon (90–100 cm footprint): 6–8 glass catfish + a small school of ember tetras or rasboras + a trio of small Corydoras.
- 40–55 gallon: 8–12 glass catfish with a larger companion school (10–15 small tetras/rasboras) and several peaceful bottom-dwellers.
Practical tips for harmony
- Provide plenty of plants and multiple hiding spots so the school can reset after scares; roomy swim lanes reduce competition during feeding.
- Feed midwater-friendly foods so the catfish and their companions are satisfied without competition from surface-only feeders.
- Introduce tankmates slowly and monitor interactions in the weeks after additions; use a quarantine tank to trial new fish if unsure.
- Rehome any fish that nip or crowd the school — protecting the group’s calm is essential for long-term success.
When you choose suitable tankmates and prioritize group size, your glass catfish will show their best, most natural schooling behavior and become a serene focal point in your freshwater aquarium.
Health, Sensitivities, and Rare Breeding Notes
Preventing disease and spotting early stress signs are the fastest ways to keep glass catfish healthy in captivity.
Remember: these mostly scaleless catfish are more vulnerable than many aquarium species. Their thin skin offers less barrier against parasites and chemical irritation, so careful, conservative treatment and steady conditions let many live into the 7–8 year range reported by experienced keepers.
Common issues and medication cautions
Watch for classic stress and disease signals: flashing (scraping), clamped fins, loss of appetite, sudden hiding, or white spots. Those signs can mean parasites (including ich), poor water chemistry, or bacterial problems — and they demand quick but gentle responses.
Medication cautions: avoid strong topical dyes and aggressive treatments that can damage delicate skin. Products like malachite green and some broad-spectrum mixes may harm scaleless fish; when treatment is necessary, choose medications known to be tolerated by sensitive species and follow dosing instructions exactly.
Quarantine, first-response, and a safe ich approach
Quarantine new arrivals for observation (commonly two weeks) and treat problems in an isolated hospital tank when possible. A typical, conservative first-line ich response is to isolate affected fish, correct water quality, and consider a carefully controlled temperature increment — but extreme heat should be used with caution on scaleless species because tolerance varies.
If medications are required, copper-based treatments (when dosed precisely and monitored) are often effective against many external parasites and can be safer than some alternatives — however, copper can still harm invertebrates and must be used with accurate test kits and regular partial water changes. Always track dosing, measure water parameters daily during treatment, and protect beneficial bacteria where possible (by avoiding complete filter media replacement).
Do / Don’t quick reference
- Do: quarantine new fish, test and correct water quality first, try non-chemical steps (water changes, improved diet, slight temp adjustments) before medicating, and consult experienced hobbyists or an aquatic vet for sensitive cases.
- Don’t: apply harsh formulas without guidance, use blanket dosages from other species, or neglect water-quality corrections as part of treatment.
Breeding reality and fry care
Breeding glass catfish in home aquariums is uncommon and often accidental. These Kryptopterus are reported as egg scatterers, but few reliable captive-spawn records exist in mainstream hobby literature. Albino or unusual color variants sometimes appear in trade, most often from specialized sources.
If fry do hatch, they require the tiniest foods: begin with infusoria or diluted liquid fry foods, then graduate to baby brine shrimp (artemia nauplii) as they grow. Frequent tiny feedings and rock-solid water parameters make the difference between success and early losses.
- Treat them like sensitive species: immediate quarantine, minimal stress, and gradual condition changes.
- Ich response path: isolate affected fish, verify water chemistry, raise temperature carefully only if tolerated, then consider measured medicinal steps with close monitoring.
- Breeding note: successful fry rearing is specialist-level — survival depends on tiny live foods and immaculate water.
When health issues arise, err on the side of gentle care: stabilize water, isolate the problem, then escalate to chemical treatments only with precise dosing and professional advice. For complicated cases, contact an aquatic veterinarian or an experienced local aquarium club before applying strong medications to these delicate glass catfish.
Conclusion
A well-kept K. vitreolus school rewards patience with hypnotic midwater motion and near‑transparent beauty — the heart of expert Glass Catfish Care.
Keep at least six in a 30+ gallon tank with subdued light, driftwood or leaf litter, and plenty of plants. Aim for gentle flow and stable water around the mid‑70s°F (≈76°F) with soft, slightly acidic to neutral parameters to reduce stress and encourage schooling.
Feed small, frequent portions — high‑quality micro pellets or flakes, daphnia, and a touch of brine shrimp — to maintain condition without fouling the aquarium. Quarantine new arrivals and prioritize water‑quality fixes first for signs of ich; use copper or other medications only when necessary and dosed precisely for sensitive, mostly scaleless catfish.
Adults reach about 3 inches, show a hidden dorsal fin, and can display internal organs through their clear bodies. With steady routines, appropriate tankmates, and stable water parameters, these Kryptopterus species turn a freshwater tank into living art.